Introduction
JsonTranslate is a multilingual JSON translation tool designed specifically for developers and content creators. It supports translation APIs from Google Translate, Azure, and DeepL(X), helping streamline internationalization and localization processes. Whether you're building multilingual websites, applications, or working with multilingual datasets, JsonTranslate provides a simple and efficient solution to translate content in JSON files into multiple target languages.
Translation Modes Overview
Global Translation
This mode recursively traverses the entire JSON structure and translates all string-type values while preserving the original JSON hierarchy and structure.
Best for:
- Translating all textual content in a full JSON file
- One-click translation without complex configurations
Targeted Nodes
Use JSONPath expressions to precisely locate one or more nodes and translate only the string values within them. Multiple paths can be separated by commas.
Best for:
- Translating only specific sections in a well-structured JSON dataset
- Improving efficiency by narrowing the translation scope in large files
Specific Keys
In this mode, you can specify particular key names for translation. Two input options are supported:
- Simple Mode: Enter key names separated by commas (English or Chinese), and the corresponding values will be translated.
- Advanced Mode: Use a key mapping component to define input-output key pairs. Translations are written to new keys, preserving the original fields.
Best for:
- Translating specific fields like
titleordescription - Keeping original data intact by outputting translations to separate keys
Notes:
- Keys are case-sensitive.
- The number of input and output keys must match; mappings will ignore nonexistent keys. At least one valid mapping is required to proceed.
- Pure numeric keys can conflict with array indices — this issue has been fixed, but avoid numeric-only keys to reduce ambiguity.
- Keys containing dots (.) are interpreted as nested paths; avoid dots in key names or rename them to prevent misinterpretation.
Selective Translation
Ideal for flat JSON structures, this mode lets you specify a starting node and target field names. The system will search from the starting point and translate all matching fields in nested objects.
Configuration Options:
- Start Key (optional): Indicates where to begin the search—useful when key order matters
- Fields to Translate: Specify target field names; separate multiple fields with commas
Best for:
- Translating fields like
"message"in flattened data structures such as logs or error reports - Simple JSON files with recurring field names requiring partial translation
i18n Mode
Designed specifically for multilingual scenarios, this mode aggregates translations under the same field structure, making it ideal for managing multilingual content for websites or apps.
How It Works
- The selected source language becomes the source field (e.g.,
zhas the source language means the source field iszh). If set toauto, the default source isen. - It scans all objects containing the source field and adds new fields for each target language at the same level.
- If a target language field already exists, it is skipped to avoid overwriting.
- When both i18n and multi-language modes are enabled, the system creates a unified JSON structure with the source and all target languages—perfect for internationalized projects.
Example
If the target languages are zh and fr, the translated result would be:
Features Overview
Mapped Translation
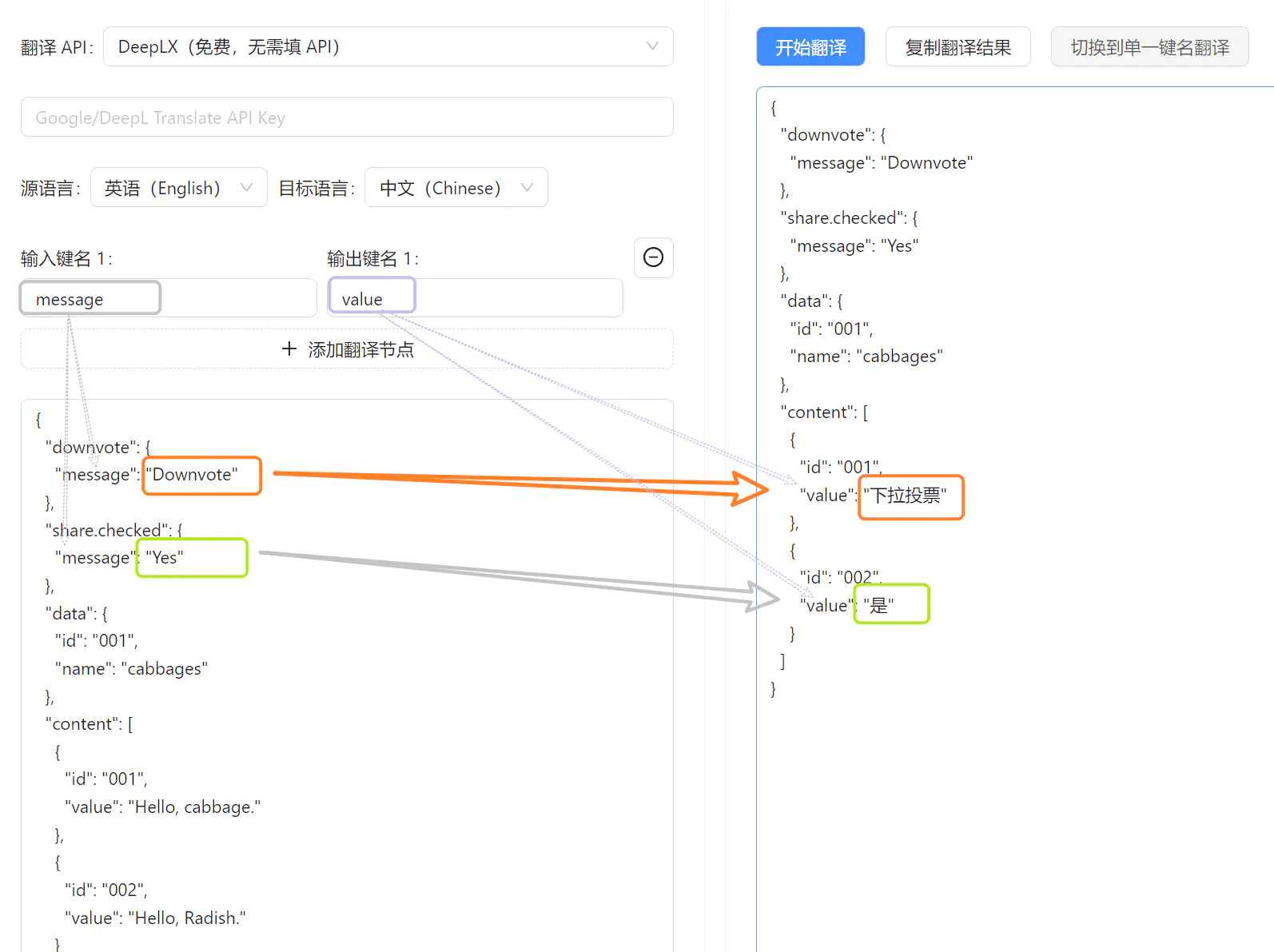
When using the Specific Keys mode, you can toggle between single-key and mapped translation modes in the results panel. In single-key mode, input and output use the same node. In mapped translation mode, translations are written to different nodes (e.g., values from Node A are translated into Node B, Node C to Node D).
How JSON Key Names Work
JSON stores data in key-value pairs. The “key” (or “name”) is a string that uniquely identifies each data item or element, making it fundamental for data access and manipulation. JsonTranslate leverages these key names for accurate translation targeting.
Here’s an explanation of several sample key names:
downvote.message: A nested key name.downvoteis a top-level key, andmessageis a key within that object.提示词.message:提示词is a key that contains an object, within whichmessageis another key.share.owner: This key includes a dot (.), but it's treated as a single key name, not a nested path. Soshare.owner.namewould incorrectly implyowneris a nested object, when in factshare.owneris one complete key.
Currently, JsonTranslate does not support JSON keys that contain dots (.). This is because dots are interpreted as delimiters in JSONPath, which may lead to misinterpretation of such keys as nested paths. To avoid this issue, it's recommended to use keys without dots.
Configuration Instructions
The application offers a wide range of translation configuration options. For detailed information, please refer to:
- Interface Overview: Features such as translation caching and multilingual translation, as well as parameters like chunk size and delay time.
- Translation API: Learn about the supported translation interfaces and AI large models.

